Zanata-cli requires User Configuration and Project-Version Configuration.
User Configuration
User configuration stores your credentials so that zanata-cli can prove to the server that requests are from you rather than an imposter. The information in your user config should be kept secret.
zanata-cli expects to find user configuration in .config/zanata.ini within your user directory.
To add configuration for a Zanata server:
- Use your favourite text editor to create or open
zanata.iniin~/.config/. - Sign into the Zanata server and navigate to the user settings page
-
Ensure that an API Key is shown. If you do not have an API Key, click 'Generate API Key' now.
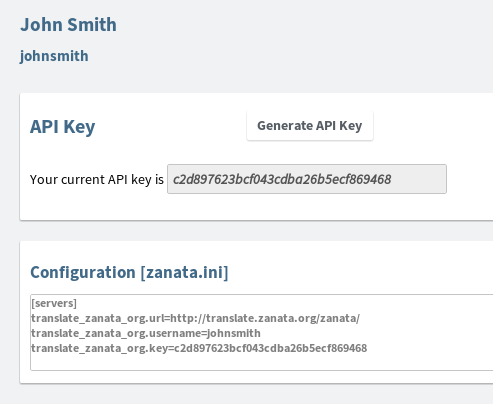
-
Copy the contents of the text-box labeled 'Configuration [zanata.ini]'.
- Paste the copied lines into
zanata.iniand save the file.
Project-Version Configuration
Project configuration stores information about a project-version, and should be kept in the project directory.
zanata-cli expects to find project-version configuration in a file named zanata.xml in the project directory.
To add project-version configuration to your project directory:
- Sign into the Zanata server and navigate to the appropriate version of your project.
-
Click the
Download config filelink to initiate download ofzanata.xml.
-
Save
zanata.xmlin your project directory.
These steps should be repeated for each project-version before using any zanata-cli commands for the project-version.
You can customize zanata.xml with command hooks so that other tools will automatically run before or after Zanata commands. Read about command hooks at the command hook.
Source directory and translation directory
To prevent the need to specify the source and translation directories on the command-line, they can be specified in zanata.xml. The source and translation directories are specified in the <src-dir> and <trans-dir> elements respectively, as shown below. Both paths must be relative to the directory that contains zanata.xml.
<src-dir>po</src-dir>
<trans-dir>.</trans-dir>
Locale Configuration
Note: Locale configuration in zanata.xml is being phased out, and this configuration will be specified on the server instead. When your project is on a server version that allows locale configuration and you have a client version that supports server locales, you should remove this configuration. Check the details in feature request 1156236.
The zanata.xml will contain a list of locales so that the client knows which locales to push and pull to/from the Zanata server. When downloaded from the Zanata server, the list will have the locales as specified by the server itself. It will look something like this:
<locales>
<locale>es</locale>
<locale>ja</locale>
<locale>fr</locale>
<locale>zh-Hant-TW</locale>
...
</locales>
Sometimes the way locales are named in your project files doesn't match Zanata's locale nomenclature, so it's necessary to create a mapping between the two. You can achieve this in the client by modifying the locale entries in zanata.xml.
For instance, if one of your files is called myfile/es.po and your project in Zanata has the es-ES locale, then your client mappng would look like this:
<locale map-from='es'>es-ES</locale>
Translation files mapping rules
You can also customize the way translation files are found when pushing, as well as the location they will be saved to when pulling.
<!-- example rules definition in zanata.xml -->
<rules>
<rule pattern="**/pot/*.pot">{locale}/{path}/{filename}.po</rule>
<rule pattern="**/po/*.pot">{path}/{locale_with_underscore}.po</rule>
</rules>
In the example above, pattern identifies a source file, and the contents of the rule element specify how translation files will be stored.
The pattern attribute is a glob matching pattern to your source document file(s). You can define more than one rule and apply each rule to a specific set of source documents using different patterns. The first matched rule will be applied to the file.
Please note pattern value will be tested against file path relative to project root, not src-dir.
pattern is optional. If not specified, the rule will be applied to all source documents in your project.
The actual rule consists of literal path and placeholders/variables.
Supported placeholders/variables are:
- {path} is the path between source document root (what you define as src-dir option) and the final file.
- {filename} the source document name without leading path and extension.
- {locale} the locale for the translation file. If you use "map-from" argument in your locale mapping, this will be the map-from value.
- {locale_with_underscore} same as above except all hyphens '-' will be replaced with underscores '_'. This is typically used in properties and gettext projects.
- {extension} the source document file extension
For example, if you have the following file structure (where {projectRoot} is the root directory of your project and contains zanata.xml):
{projectRoot}/
templates/messages/kdeedu/kalzium.pot
templates/messages/kdeedu/artikulate.pot
de-DE/messages/kdeedu/kalzium.po
de-DE/messages/keeedu/artikulate.po
...
zanata.xml
Here we have two source documents (with "pot" extension) and two translation documents (with "po" extension) for the locale "de-DE".
You can then use below configuration:
<src-dir>templates</src-dir>
<trans-dir>.</trans-dir>
<rules>
<rule pattern="**/*.pot">{locale}/{path}/{filename}.po</rule>
</rules>
Explanation: Since you have defined <src-dir> as templates, the source document templates/messages/kdeedu/kalzium.pot will have its path extracted relative to {projectRoot}/templates, which gives the relative path messages/kdeedu/kalzium.pot. The relative path then will be partitioned into several tokens to form the following variables:
{path} = 'messages/kdeedu/'
{filename} = 'kalzium'
{locale} = 'de-DE'
{locale_with_underscore} = 'de_DE'
{extension} = 'pot'
NOTE the relative path
messages/kdeedu/kalzium.potwill be the document's unique identifier inside Zanata. If you changesrc-dirsetting later, e.g. to ".", which results in a change of the relative path totemplates/messages/kdeedu/kalzium.pot, pushing again will create a new document with the new path as its unique identifier, and the old document will be considered obsolete and will not be visible to anyone. The old document's translations will not be copied to the new document automatically, but they will appear as Translation Memory matches. This can be confusing and frustrating for translators.
As the rule is defined as {locale}/{path}/{filename}.po, for locale de-DE,
- source file kalzium.pot's translation file will be written to or read from
{projectRoot}/de-DE/messages/kdeedu/kalzium.po. - source file artikulate.pot's translation file will be written to or read from
{projectRoot}/de-DE/messages/kdeedu/artikulate.po.
You can also replace {locale} with {locale_with_underscore} if you want all your locales to use underscore instead of hyphen. e.g. de-DE will become de_DE which results in translation files written to or read from {projectRoot}/de_DE/messages/kdeedu/kalzium.po.
The mapping rules configuration is optional in zanata.xml. If not specified, standard rules are applied according to your project type.
- gettext:
{path}/{locale_with_underscore}.po - podir:
{locale}/{path}/{filename}.po - properties:
{path}/{filename}_{locale_with_underscore}.{extension} - utf8properties:
{path}/{filename}_{locale_with_underscore}.{extension} - xliff:
{path}/{filename}_{locale_with_underscore}.{extension} - xml:
{path}/{filename}_{locale_with_underscore}.{extension} - file:
{locale}/{path}/{filename}.{extension}